The Role of Health Care Workers of Kedungrejo Public Health Center in Stunting Reduction Strategy
Main Article Content
Abstract
Introduction: Banyuwangi Regency experienced the increase of stunting number as many as 8,2% from 2019. Stunting is not only affecting toddlers’ health, but also obstructing the development and the progress of a nation in the future. This case relates to the role of the health human resources in solving stunting. The role of health human resources towards stunting reduction strategy is crucial, in which using specific and sensitive nutritional intervention strategies. The current study aims to analyse the role of health human resources towards stunting reduction strategy.
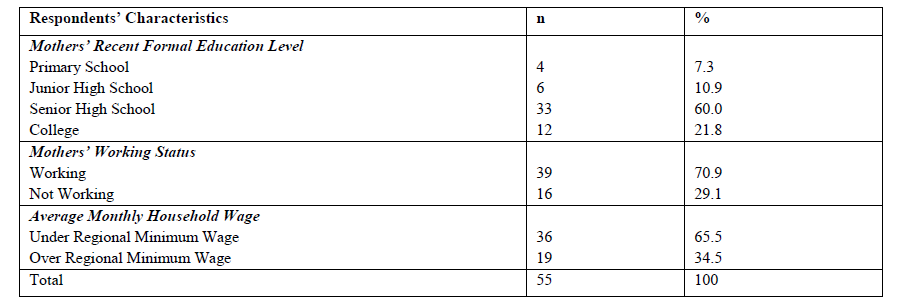
Methods: The study performed an analitical observational research with a cross sectional approach. The sample was 55 mothers possessing 0-23-month toddlers taken by clustered random sampling. The research variable was the basic role of the health human resources with some indicators applying specific and sensitive nutritional intervention. The data were analysed using descriptive method and logistic regression test.
Results: The role of the communicator was mostly in a good category (61.8%), the motivator was mostly in good category (80%), the facilitator was mostly in not really good category (54.4%), the counselor was mostly in good category (76.4%). The communicator and the motivator influenced the specific nutritional intervention. The motivator and the facilitator influenced the sensitive nutritional intervention.
Conclusion: The role of the communicator and motivator influenced the specific nutritional intervention as the stunting reduction strategy. Also, the motivator and facilitator influenced sensitive nutritional intervention.
Article Details
References
UNICEF; WHO; World Bank Group. Levels and Trends in Child Malnutrition: Key Findings of the 2019 Edition. 2019.
Kementerian Kesehatan Badan Penelitian dan Pengembangan Kesehatan. Hasil Utama Riskesdas 2018. 2018.
Dinas Kesehatan Kabupaten Banyuwangi. Jumlah Kasus Gizi Buruk pada Balita di Kabupaten Banyuwangi Januari-November 2019. 2019.
Ministry of Health of Indonesia. Statute of Indonesian Republic Number 36 of 2009 about Health. 36 Indonesia; 2009.
Ministry of Health of Indonesia. Minister of Health Regulation of the Republic of Indonesia. 1231/Menkes/Per/XI/2007 Indonesia; 2007.
Kementerian Kesehatan RI. Pedoman Indikator Program Kesehatan Masyarakat dalam RPJMN dan Renstra Kementerian Kesehatan Tahun 2020-2024. Jakarta; 2020.
Kementerian Kesehatan RI. Profil Kesehatan Indonesia 2018. Jakarta; 2019.
Husnaiyah D, Yulyanti D, Rudiansyah. Hubungan Tingkat Pendidikan Ibu dengan Kejadian Stunting. Indones J Heal Sci. 2020;12(1):57–64.
Djogo HMA, Betan Y, Dion Y. Hubungan Pekerjaan Ibu dan Praktik Asi Eksklusif dengan Kejadian Stunting pada Balita di Kabupaten Timor Tengah. J Kesehat. 2020;8(1).
Julianti E, Elni. Determinants Of Stunting in Children Aged 12-59 Month. Media J Nurs. 2020;10(1):36–45.
Li Z, Kim R, Vollmer S, Subramanian. Factors Associated with Child Stunting, Wasting, and Underweight in 35 Low- and Middle-Income Countries. JAMA Netw Open. 2020;1(1):1–18.
Izah N, Zulfiana E, Rahmanindar N. Effect Of Family Characteristics on Stunting Events in Toodlers Aged 6-59 Month. Midwiferia J Kebidanan. 2020;6(1):47–51.
Fajrianti D, Yunitasari E, R. P. The Correlation betwen Personal Reference: Health Workers and Health Facilities with Parenting in Stunting Prevention. Pediomaternal Nurs J. 2020;6(2):125–32.
Potter PA, Perry AG. Buku Ajar Fundamental Keperawatan: Konsep, Proses, Dan Praktik. 4th ed. Jakarta: EGC; 2007.
Wahyunnisa SA, Handayani N, Nadatien I. Gambaran Peran Tenaga Kesehatan sebagai (Advocator, Educator, Motivator Dan Fasilitator) dalam Sosialisasi Imunisasi Pentavalen di Puskesmas Gayungan Surabaya. 2018;
Safitri CA, Nindya TS. Hubungan Ketahanan Pangan dan Penyakit Diare dengan Stunting pada Balita 13-48 Bulan di Kelurahan Manyar Sabrangan, Surabaya. Amerta Nutr. 2017;1(2):52–61.
Laili AN, Munawir A, Ningtyas. Food Intake and Food Security as Determinants of Stunting Children Under Five Years. Heal Notions. 2017;1(1):1–9.
Hizriyani R, Aji TS. Pemberian Asi Ekslusif Sebagai Pencegahan Stunting. J Jendela Bunda. 2021;8(2):56–62.
Damayanti RA, Muniroh L, Farapti. Perbedaan Tingkat Kecukupan Zat Gizi dan Riwayat Pemberian Asi Eksklusif pada Balita Stunting dan Non Stunting. Media Gizi Indones. 2017;11(1):61–9.
Sari NAM, Resiyanthi NK. Kejadian Stunting Berkaitan dengan Perilaku Merokok Orang Tua. J Ilmu Keperawatan Anak. 2020;3(2):24–30.
Kwami CS, Godfrey S, Gavilan H, Lakhanpaul M, Parikh P. Water, Sanitation and Hygiene: Linkages with Stunting in Rural Ethiopia. Int Journl Environ Res Public Heal. 2019;16(20):21.
Otsuka Y, Agestika L, WIdyarani, Sintawardani N, Yamauchi T. Risk Factors for Undernutrition and Diarrhea Prevalence in a Urban Slum in Indonesia: Focus on Water, Sanitation and Hygiene. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2019;100(3):727–32.
Fregonese F, Siekmans K, Kouanda S, Druetz T, Ly A, Diabate S, et al. Impact of Contaminated Household Enviroment on Stunting in Children Aged 12-59 Month in Burkina Faso. J Epidemiol Community Health. 2017;71(1):356–63.
Olo A, Mediani SH, Rakhmawati W. Hubungan Faktor Air dan Sanitasi dengan Kejadian Stunting pada Balita di Indonesia. J Pendidik Anak Usia Dini. 2020;5(2):1113–26.
Setyawati VA, Ramadha F. Pengaruh Kampung KB pada Intervensi Gizi Sensitif Stunting di Desa Janegara. J Gizi Indones. 2020;9(1):42–7.
Restiyani NL, Yasa IG. Efektivitas Program Kampung Keluarga Berencana (KB) dan Dampaknya Terhadap Kesejahteraan Keluarga Miskin di Kota Denpasar. E-jurnal Ekon dan Bisnis. 2019;8(7):711.