Evaluation of Thyroid Trace Elements in Hashimoto's Thyroiditis Using Method of X-Ray Fluorescence
Main Article Content
Abstract
Background: Role of trace elements (TE) in etiology and pathogenesis of Hashimoto's thyroiditis (HT) is unclear. The aim of this exploratory study was to assess whether there were significant changes in thyroid tissue levels of six TE (Br, Cu, Fe Rb, Sr, and Zn) are present in the autoimmune transformed thyroid.
Methods: Six TE of thyroid tissue were determined in 8 patients with HT and 105 healthy populations. The measurements were performed using energy-dispersive X-ray fluorescent analysis.
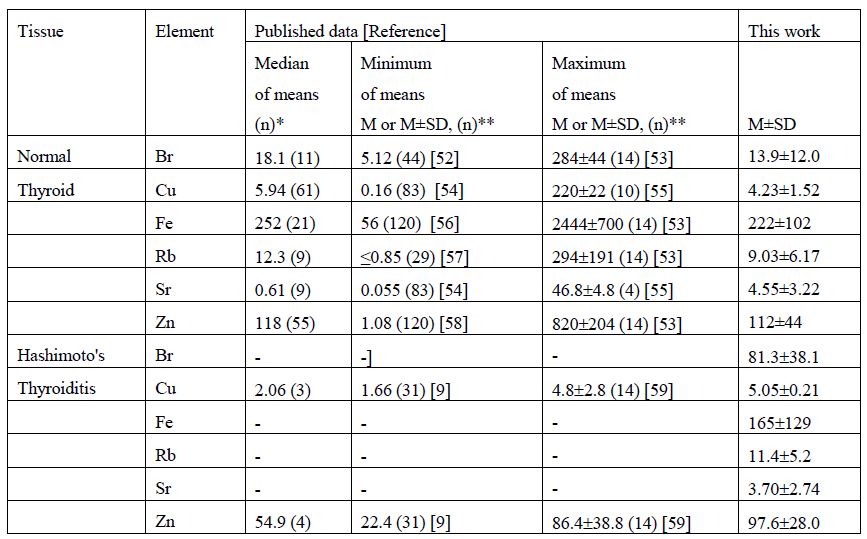
Results: Elevated mean values of Br and Cu content were found in thyroid with HT in comparison with normal level (in approximately 5.9 and 1.2 times, respectively).
Conclusions: There are considerable changes in some TE contents in tissue of thyroid with HT. Thus, it is reasonable to assume that the levels of these TE in thyroid tissue can be used as HT markers. However, this topic needs additional studies.